CHUOSILIKA
-
Fine Powders

Applications
- Fillers for silicone gums, resins, paints, etc.
Products Handled
- • Silika #6B
- • Oplite W-3005S
- • Oplite W-3005K
-
Fired Products

Applications
- Used in the beer-making process, the refined sugar-making process, and other applications that require filtering for clarity
Characteristics
- 1. Fired at 800 to 1200°C, the temperature at which organic matter is completely immolated
- 2. Can filter effectively and quickly thanks to the sintering effect of firing
Products Handled
- • Silika #300S (for clarity)
Used in filtering requiring high clarity - • Silika #300S-A (for clarity)
Used in filtering that requires higher clarity of filtrate than with Silika #300S - • Silika #100F (for high clarity)
Used in filtering that requires extremely high, sparkling clarity of filtrate
-
Flux-Fired Goods

Applications
- Medium and high-speed filtering in everything from food products to general industry applications
Characteristics
- 1. Fired at 800 to 1200°C with a small amount of added sodium carbonate
- 2. A more stable structure thanks to the sodium carbonate reaction with the SiO2 in diatomaceous earth, forming a thin glass coating on the particle surface
- 3. More than 10 times the transparency of fired products
Products Handled
- • Silika #645, Oplite W-3050 (for high-speed use)
Used in filtering of fluids with high solid content, fluids that are difficult to filter, and high-viscosity fluids - • Silika #600H (for medium-speed and general use)
A standardized type used for moderate filtration and moderate clarity - • Silika #600S, Oplite W-3020 (for medium-speed and clarity use)
Used in applications that require higher clarity of filtrate than with Silika #600H - • Silika Pool Ace
A medium-speed/general-use filtering aid for use in infinity pools
Example Filtration Applications of Fired Products and Flux-Fired Products
Used in various types of water treatment, including for sugars, cornstarch, alcoholic drinks such as beer and wine, soy sauce, seasonings, various fruit juices, various plant extracts, plant oils, mineral oils, agar-agar, gelatin, antibiotics, enzymes, solvents, medicines, chemical products, etc.
-
Dry Powders

Applications
- Building materials, heat insulating material, anti-caking agents for complex fertilizers, agrochemical carriers, etc.
Characteristics
- 1. Utilizes the special properties of diatomaceous earth
- 2. Viscosity-adjusted products to meet customer needs
- 3. Can be used across a wide range of applications, such as building materials or heat insulating material that use the calcium silicate reaction, as anti-caking agents for complex fertilizers, or as agrochemical carriers
Products Handled
- • Oplite P-1200
- • Oplite P-1300
-
What is Diatomaceous Earth (Silica)?
Diatomaceous earth is a solid substance made by smelting fossils of an algae (chrysophyceae) called “diatom” that thrived in ancient times.
Diatomaceous earth is the fossil of diatom, an algae (plant plankton) that lived in ancient times, from several tens of thousands of years to several thousand years ago. Diatom was a unicellular plant of only about several dozen micrometers in size. It had countless pores of 0.1 to 1.0 micrometers along the cell membrane, which it used to take in water. At the end of a long era, diatom plants underwent mass extinction and were deposited as sediment, leaving siliceous remains called diatom shells, which were fossilized and became diatomaceous earth.
Diatomaceous earth is composed mainly of silicone dioxide (SiO2), the same substance as glass. Thanks to diatom’s unique configuration and chemical stability, it has excellent absorptive and adsorptive properties. In ancient Greece, it was used as an abrasive and in making lightweight bricks. In Japan, it has traditionally been used as a paint primer for Wajima lacquerware since the Edo period. Also, the Hagia Sophia cathedral in Istanbul, Turkey, is known as the oldest building constructed using diatomaceous earth. Diatomaceous earth was also famously used by Sweden’s Professor Alfred Nobel to absorb nitroGlycerine in order to create dynamite.
The best use for refined diatomaceous earth is as a filter aid. It can separate suspended solid content from a high-turbidity stock solution to achieve a clear filtrate. When performing body feeding during filtration operation, diatomaceous earth can decrease the filtration resistance to extend the life, making it the most effective method to reduce costs. Diatomaceous earth has better properties as a filter aid than its competitor, perlite, and the rich variety of its permeability (capture) performance opens up uses in a wide variety of fields.
-
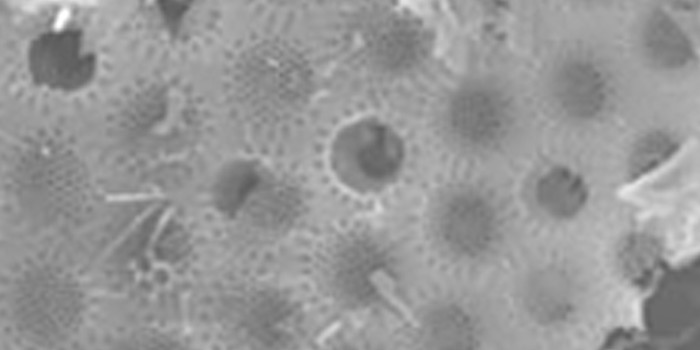
Electron microscope photo
-

Electron microscope photo (enlarged)
-



